Tutorial 2: Mental Health Assessment
At the end of the tutorial today, you should be able to:
a.Understand the process of biopsychosocial mental health assessment and its importance for mental health nursing
b.Conduct a mental state examination (MSE) and understand its purpose and application in clinical practice
c.Identify types of risk through the use of assessment
d.Understand the use of screening tools and their place in the assessment process
e.Apply the 5 P’s to present a clinical formulation
f.Begin to understand care planning and nursing interventions for mental health issues.
NSB204 Mental Health Assignment-Australian College Mental Health Nurses.

Resource requirements:
Whiteboard and pens
Tutorial Plan
Slide 3: Listen to
John Lennon wrote this song and it was a surprise to the band at the time, even when surrounded by people MI can be missed. He spent his last years in personal isolation for 5 years struggle with MH and depression Help me
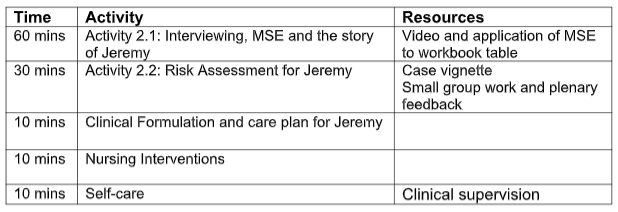
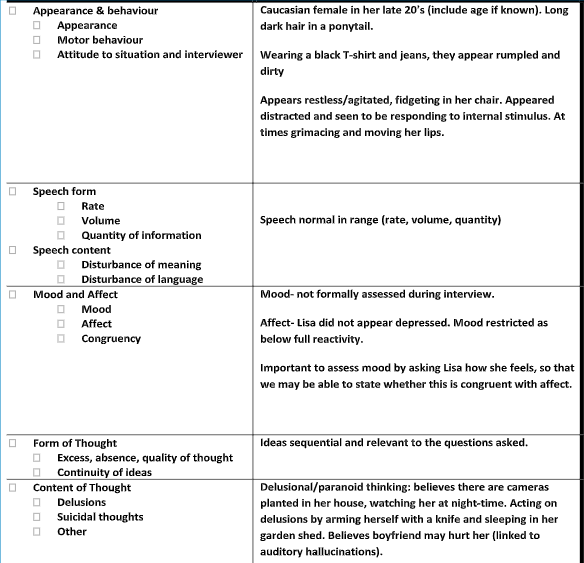
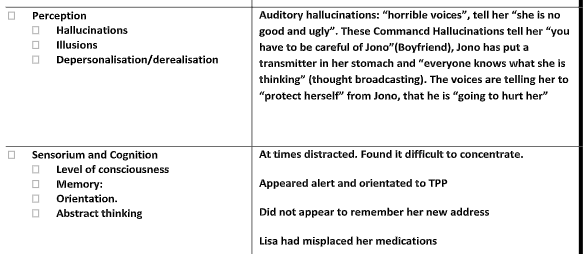
Activity 2.1 Interviewing, MSE and the story of Lisa
Patient/client and consumer are used interchangeably to reflect the varying preferences of persons receiving care.
Assessment is the first step in the process of any healthcare setting to establish the needs of the person. In mental health nursing the goal of the assessment is to:
- Establish a therapeutic alliance with the person and any support persons recognised by the patient
- Collect information about the persons mental state that is reflected in the components of the MSE
- Develop understanding of the person’s needs in the current context
- Develop a formulation to enable collaborative care to be offered
- Develop a nursing care plan in collaboration with the person and/or any other nominated support persons
- Decrease the negative impact of psychiatric symptoms for the person and or support networks
- Provide a baseline of information from which later assessments can be compared
Before the interview begins there are some basic requirements.
1.Wherever possible, the interview should be carried out in a room that is reasonably quiet and likely to be free of interruptions.
2.The seating and other furniture should be arranged to enable face-to-
face communication. The seating should also be arranged so that you are
able to exit the room in a hurry if necessary (i.e. you are not trapped in a
corner).
3.The safety of both client and staff has been considered.
4.You have a clear purpose for carrying out the interview and the person/client is aware of what this is.
5.The client is capable of participating, for example they are not intoxicated,excessively agitated or reduced level of consciousness.
Interpreters/parents may need to be present.
NSB204 Mental Health Assignment-Australian College Mental Health Nurses.
At all interviews we need to consider the roles played by both of you, the
relative appearance of power between you and the other person and of course gender and cultural issues. It is therefore, important for us to try and minimise the potential negative impacts of these factors as much as possible.





This is a video of Lisa being interviewed. There are two key learning experiences attached to this:
Completion of an MSE for Lisa using the guidelines as provided in the workbook; &Observations about the establishment of the therapeutic relationship.

Clinical Formulation
Summarize the pertinent information from case study
Presenting
factors
Activity 2.2 – Risk Assessment
Lisa
Work through the case study in small groups and complete a risk assessment for Lisa focus on one domain in risk.
Using chat:- have students write up feedback on one domain of risk from the following four:
harm to self
harm to others
vulnerability
absconding (treatment engagement).
Assess the static and dynamic risk factors for the domain you have been allocated, as well as any protective factors that you identify.
Lisa
Lisa is admitted to hospital, where she remains for two weeks and is then discharged to the community on Treatment Authority. While in hospital she was commenced on oral medication: Olanzapine 5mg mane which was then titrated to 10mg daily, with PRN medication of Lorazepam 1-2mg QID [max 8mg]. On discharge Lisa is tolerating the Olanzapine 10mg and is not requiring any PRN medication. She has a Mental Health Clinician who visits regularly. Lisa returns to living in her home environment with the support of her family and Jono, her boyfriend.
As Lisa’s Clinician you attend her house for a routine home visit two months post discharge. On this visit, she presents as dishevelled with weight loss, and says she hasn’t been sleeping for the past 4 days. She says she has no appetite and can’t remember the last time she ate anything. She admits that she has been using speed again and is only taking her medication “when she remembers”, although she fears ‘this may be poisoned”. She then explains that her relationship with Jono has broken down and that he has left her. She says ‘just as well, because she might have done something to him if he had not”.She does not explain further about this. She says she is staying in the shed again as the cameras “are everywhere”.
A chat with her parents reveals they are very concerned about Lisa and remember that the last time she spoke like this she ended up in hospital for a long time. They corroborate that she has not been sleeping, has been using drugs and disappearing at night for long periods. They have tried to talk to her about it but she becomes distressed. During a recent visit, Lisa accused her parents of ‘being in on it” and asked them not to come back
to her house.
Although Lisa remains pleasant towards you, she appears confused and unable to concentrate.
Questions for discussion:
1.What is Lisa likely/unlikely to do if no interventions occur?
2.How soon might these happen?
3.What might the consequences be and what are the potential impact of these?
4.What could be useful to mitigate these risks?
Activity 2.3 – Clinical Formulation (The 5 P’s)
A core part of a comprehensive mental health assessment is the clinical formulation.
The formulation is a way for the client and the nurse to work together to find out what has happened to the person, what it means to them and what steps can be taken to relieve distress, address issues and fulfil their needs.
The formulation is a way to organise the information collected during the Mental Status Examination and during the collection of the bio-psycho-social assessment and personal history of the client. The formulation broadly aims to answer the questions ‘why this person?’, ‘why this problem?’, ‘why at this time’?
The formulation organises information into presenting, predisposing, precipitating, perpetuating and protective factors that are relevant to the person’s clinical presentation.
It is commonly known as the 5 P’s.
- Presenting factors: the primary concerns the individual person has presented with at this time.
- Precipitating factors: events that have occurred in the last seven days that led to the current presentation for help e.g. Marriage breakup, job loss, conflict, etc.
- Predisposing factors: events that have occurred across the person’s life time that have led to the development of mental health concerns e.g. child abuse,trauma history, developmental difficulties, etc
- Perpetuating factors: factors that might limit the person’s ability to cope and to address issues i.e. Drug/alcohol use, disengagement from treatment, lack of insight and judgment, etc.
- Protective factors: people, events and personal strengths that enable the person to continue to progress i.e. supportive relationships, work, engagement in treatment, etc.
Activity: Reflect on the video you have just watched and the risk assessment scenario to conduct the MSE and get students to give examples of each factor using the table below for Lisa.
Summarise the relevant information gleaned from the video/
clinical scenario for Jeremy
Presenting factors, Precipitating factors,Predisposing factors,Perpetuating
factors, Protective factors.
Activity 2.4 Nursing Interventions
Refer to recommended text, Lippincott’s manual of Psychiatric nursing care plans.
How does the formulation inform nursing interventions for Lisa?
Begin the process of exploring nursing care planning as a part of the mental health nursing process. Reflect on how it differs from other nursing experiences you have had thus far. What aspects are similar?
Nursing interventions:-
Rational:-
Nursing interventions:-
Rational:-
Nursing interventions:-
Rational:-
Nursing interventions:-
Rational:-
2.5 Clinical Supervision and Self -care strategies
Link to Dr Jan Kabat-Zinn defines mindfulness and describes the benefits of being present to the moment
The Australian Clinical Supervision Association (ASCA) presents thei definition of clinical supervision
“Clinical supervision is a formal professional relationship between two or more people in designated roles, which facilitates reflective practice, explores ethical issues, and develops skills”.
NSB204 Mental Health Assignment-Australian College Mental Health Nurses.
Here are a few examples: Self evaluation – This is the process of reflecting on your own skills, your professional strengths and limitations. …
Within supervision, nurses can enhance their skill and knowledge base, ensure responsible and ethical practice and monitor their self-care and professional competence.
What do you discuss with your clinical supervisor/mentor?
Case review
Ethical issues, including boundaries
Legal issues, including things like mandated reporting
Counter- transference
Use of self in clinical work
Diagnostic skills
Treatment planning
Interventions.
NSB204 Mental Health Assignment-Australian College Mental Health Nurses.



